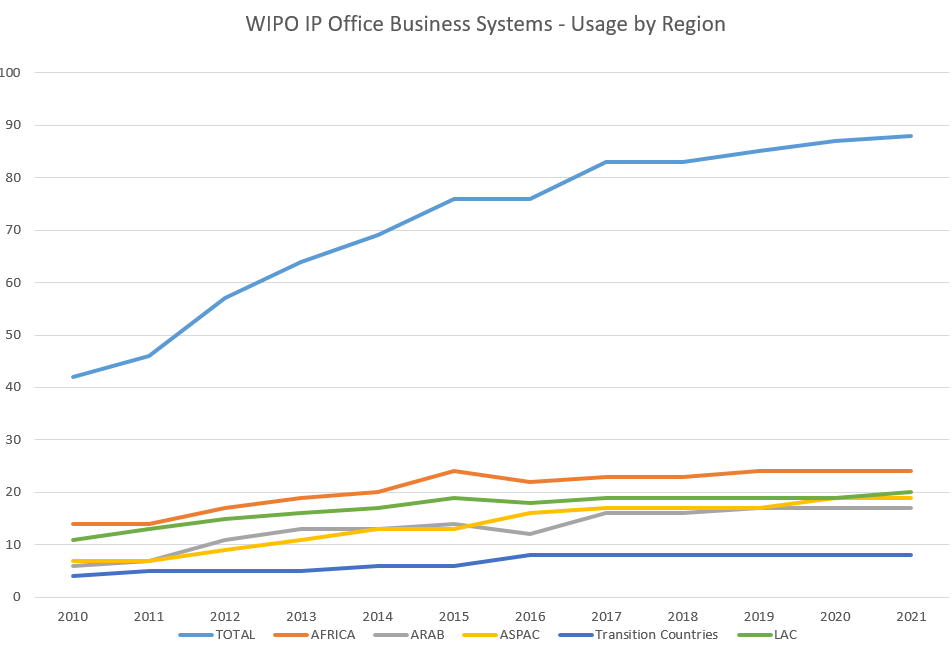
IP Office Business Solutions
WIPO’s program of assistance to intellectual property (IP) offices provides business systems for national and regional institutions in developing and least developed countries (LDCs), enabling them to participate effectively in the global IP system. It aims to help IP offices deliver better services to their stakeholders through:
- online services, including search, registry and filing systems;
- efficient and standardized business processes for IP administration;
- integration into regional and international IP systems to enable the digital exchange of data and documents.
IP office support Wiki
Our wiki site provides access to technical documentation on products, specifications and new features developed for and deployed in national IP offices, as well as software repository installation and change documentation. (Authorized users only.)